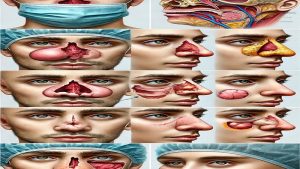
Comprehensive Nasal Reconstruction Review After Tumor Removal
Introduction
Nose regeneration After removing the tumor is a complex and sensitive process aimed at restoring the natural appearance of the nose, improving respiratory function and maintaining symmetry and facial beauty.. The nose requires high care and skill in regeneration due to the central position in the face and complex structure including the skin, cartilage, bone and mucosa, after removing the tumor.. In this article from the site of Dr. Behnam Khorrami (Isfahan nose surgeon _ Jaw surgeon of Isfahan), Will examine the types of nasal tumors, methods of removing them, and post -surgical reconstruction techniques.
Structure and function of the nose
The nose of the three-layer is formed principal:
- The outer layer (Skin): Protective coating that operates against injuries and environmental factors.
- The middle layer (Cartilage and bone): Support framework that determines the shape and strength of the nose.
- Inner layer (mucus): The interior coating that is responsible for moisturizing air and filtering particles.
Nasal reconstruction after tumor removal requires precise repair of these three layers to restore beauty and natural function..
Types of nose tumors
1. Skin tumors
These tumors usually originate from nasal epidermal cells and are divided into benign and malignant categories.:
Basal cell carcinoma (BCC): The most common skin tumor that grows slowly and usually does not metastasis.
Cobalt cell carcinoma (SCC): More aggressive than BCC that may extend to deeper tissues.
Melanom: A type of malignant tumor that originates from skin melanin cells.
2. Car cartilage and bone tumors
Kendroskoma (Chondrosarcoma): Malignant cartilage tumor that usually develops in the nasal septum.
Osteoskoma (Osteosarcoma): Malignant bone tumor that attacks bone tissues.
3. Soft tissue tumors
A hemangioma: Benign tumor derived from blood vessels.
SACCUMA: Tumor of connective tissue that is aggressive and may extend to the surrounding tissues.
Removal methods Tumor
1. Mohassa Surgery (Mohs Surgery)
The most common way to remove skin tumors, especially BCC and SCC.
In this method, the tissue is removed in a layer and at each step with the microscope to ensure complete removal of the tumor..
2. Complete removal with safe margins (Wide Excision)
In this method, the tumor tissue is removed with a margin of the healthy tissue around it..
This procedure is suitable for deep malignant tumors such as melanoma or sarcoma.
3. Endoscopic surgery
Is done for internal tumors of the nose or sinuses.
This method is low -invasive and is done through the nose using a camera and special tools..
The principles of nasal reconstruction after removal of the tumor
Nose reconstruction depends on the three basic principles:
- Structural repair: Restore the strength and shape of the nose using cartilage and bone bond.
- Functional repair: Maintain or restore normal respiratory function.
- Aesthetic repair: Create a natural appearance with proper symmetry and fit with the face.
Nasal reconstruction techniques
1. Reconstruction with cartilage transplantation
Cartilage is usually harvested from the following areas:
Ear
The ribs
Cartilage to repair septum, blades and Tip of the nose Used to be.
2. Regeneration with bone grafting
Bone is usually harvested from the following areas:
Skull
The ribs
Other parts of the nose
Used to rebuild the bridge and the main nose framework.
3. Skin flaps (Skin Flaps)
Forehead flap (Forehead Flap):
Use of forehead skin to regenerate large nasal parts.
This flap offers natural results due to the color and texture of the nose..
Nazolbial flap (Nasolabial Flap):
The use of the skin of the area next to the nose.
Suitable for rebuilding blades and sides of the nose.
4. Skin transplant (Skin Grafts)
Skin from other areas of the body (Like the back of the ear, arm or thighs) It is removed.
Used to repair nasal surface coating.
Reconstruction steps
- first stage: Complete tumor removal and survey of residual tissues to ensure complete elimination of cancer cells.
second stage: Repair of nasal structure with cartilage and bone bond.
third level: Reconstruction of skin layers using skin flaps or skin transplantation.
The fourth stage: Final reforms to improve respiratory function and natural appearance.
Challenges in nose reconstruction
Reduce blood supply: After the tumor removal, blood flow to the nose may decrease.
Mismatch: Matching the color of the forehead or other areas with the nasal skin is challenging.
Reduce respiratory function: Incorrect regeneration may cause nasal duct obstruction.
Results and prognosis
Structural success: Using cartilage and bone, the natural shape of the nose is usually returned.
Performance improvement: Restore natural respiratory function by reconstruction of septum and nasal ducts.
Aesthetic satisfaction: If the reconstruction is done carefully, the beauty results are usually satisfactory.
Conclusion
Nasal reconstruction after tumor removal is a complex and specialized process that requires a deep understanding of anatomy, surgical skills and aesthetic art.. The use of advanced techniques such as cartilage transplantation, bone, skin flaps and skin transplantation improves respiratory function, restore natural structure, and achieve excellent aesthetic results.. Cooperation between plastic surgeon, ear and nose surgeon (ENT) And dermatologist is essential to improve the final results.
Useful links:
Isfahan nose surgeon _ Jaw surgeon of Isfahan
Dr. Behnam Khorrami's page in the clinic 24 | Maxillofacial surgeon in Isfahan clinic 24 | Nose surgeon in Isfahan clinic 24
Dr. Behnam Khorrami, nose surgeon in Isfahan at Dr. Af | Maxillofacial surgeon in Isfahan at Dr. Af | Isfahan nose surgeon at Dr. Af